Appearance
Realm Console
Create Collector
- In Realm, go to Collectors > Add Data Collector
- Type a name for your collector, which typically represents the data center where the collector will be running. For example "US-East Collector"
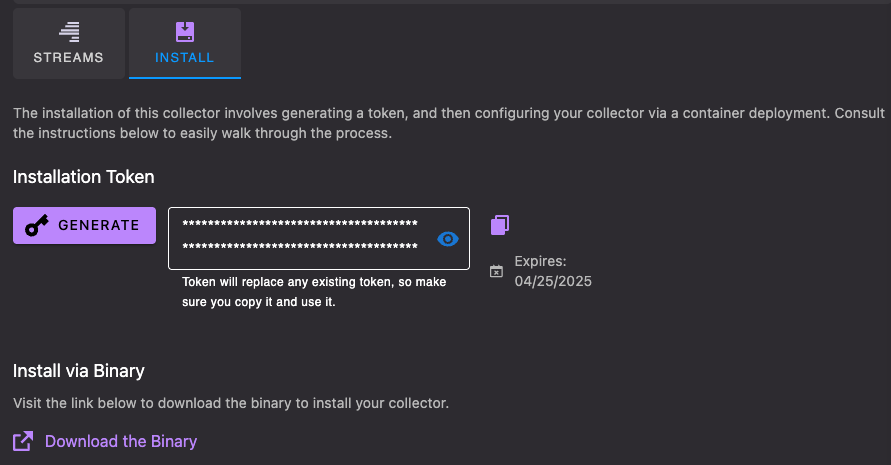
- From your collector page, go to the Install tab and Click Generate
- Copy the collector install token, you will need it later when installing the collector
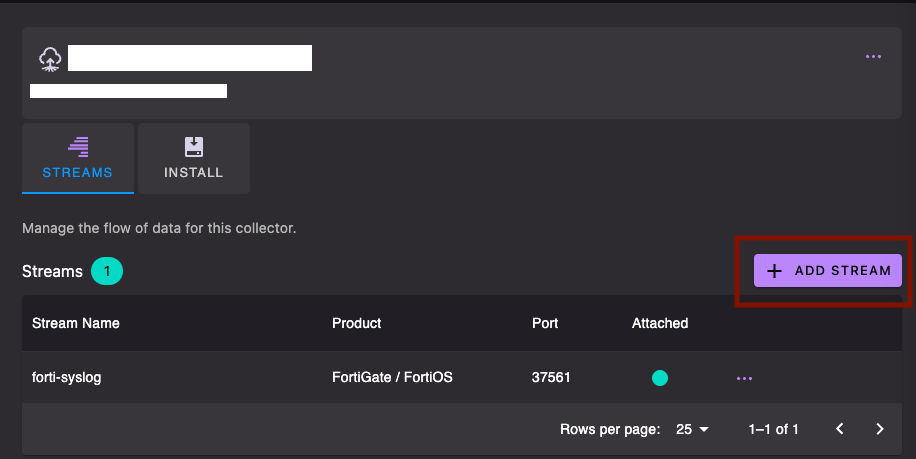
Create Streams
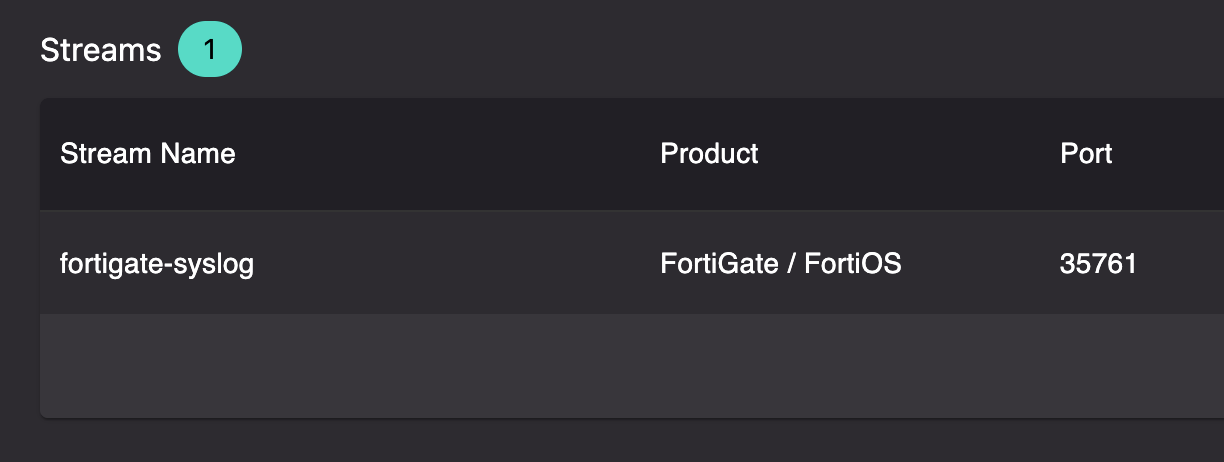
- Click Add Stream from your Collector page
- Name the stream, this typically matches the device/appliance generating the logs (such as a firewall, DNS router etc)
- Choose the product you want to stream, such as "Fortigate"
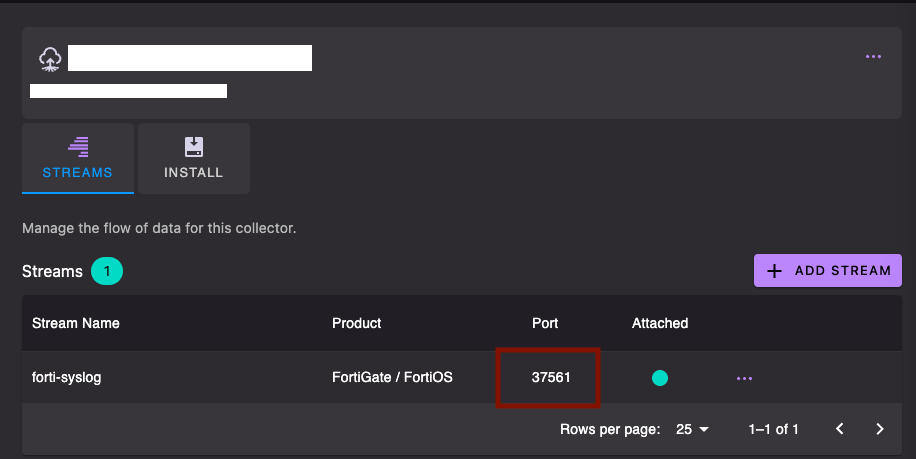
- Note down the receiving port for the data
Install Realm Collector
Realm collector is an Open Telemetry Collector (OTel) distribution. Realm collector is typically setup to run on a VM/container.
VM Requirements
- 64-bit processor (Intel or AMD)
- 2 GB memory for a load of 10,000 events/sec. For higher log volume, allocate more memory to the VM.
- 50 GB free disk space
- Linux, Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 or above. Installing the collector as a Windows service requires administrator access.
- Static IP address or a DNS name
Outbound IP/Port Allow List
Realm collector uses the following FQDN/IPs and ports for network communication. In restricted/locked down networks, it is typically necessary to punch a hole through the firewall to allow these connections.
- Inbound: Port is user-defined in Realm Console.
- Outbound: Here are the three URLs that the collector communicates over with Realm backend.
Protocol: TCP
Port: 443
IP Addresses:
text
18.220.219.115
13.58.136.153
3.143.123.136
3.139.32.204
3.140.52.245
13.59.168.65FQDN: api.realmsec.us
- Purpose: Collector uses this endpoint to periodically poll for config updates.
FQDN: *.otlp.ingest.realmsec.us
- Purpose: This is the data ingestion endpoint. Collector sends all log data to this endpoint.
FQDN: health.ingest.realmsec.us
- Purpose: Collector sends its operational metrics for health monitoring to this endpoint.
Deployment topology
Either of the following strategy works each with its pros and cons.
- Configure multiple log sources (from the same vendor) to send logs to a single Realm collector on the same receiving port (ie. same stream defined in realm console). Benefit of this approach is that it makes it easy to track
- Each firewall can be configured to send logs to a distinct port on the Realm collector, if necessary.
Downloads
Collector binaries for all platforms, including Linux, are available from GitLab Releases.
The latest collector release is v0.137.0-rlm4.
Install on Windows
- Download the .exe https://gitlab.com/realm-security-public/collectors/-/releases
to a suitable temporary location, such as
C:\Users\Administrator\Downloads\realm-collector-amd64.exe
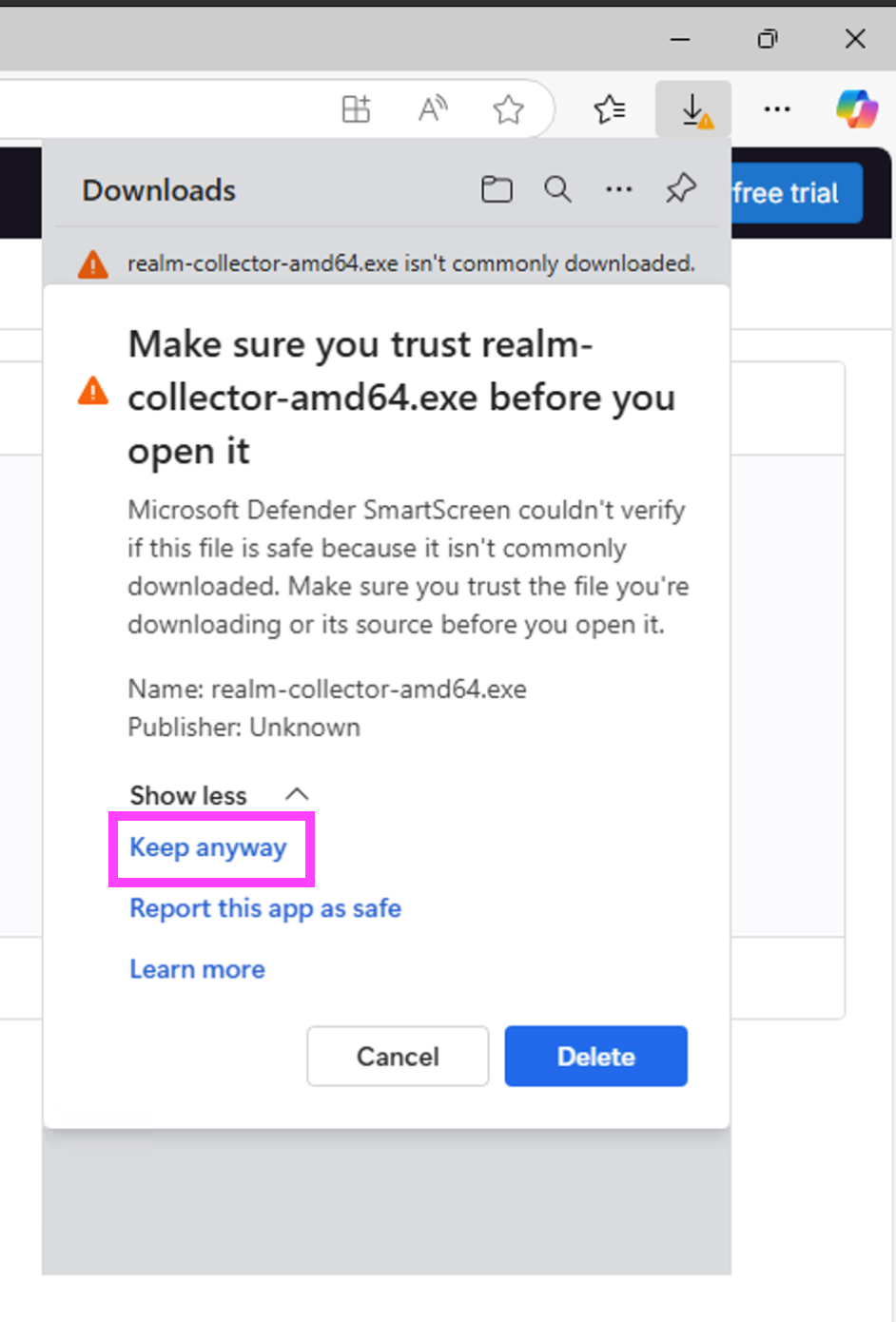
- Open an Administrative terminal
- Open Start menu, search for "Terminal" (called "Windows PowerShell" or "Command Prompt" on older versions)
- Right click and choose "Run as Administrator"
- Run the collector with the install token
cd Downloads
.\realm-collector-amd64.exe --config realm:<TOKEN>At this point the collector is setup to run as a windows service.
Update Host Firewall
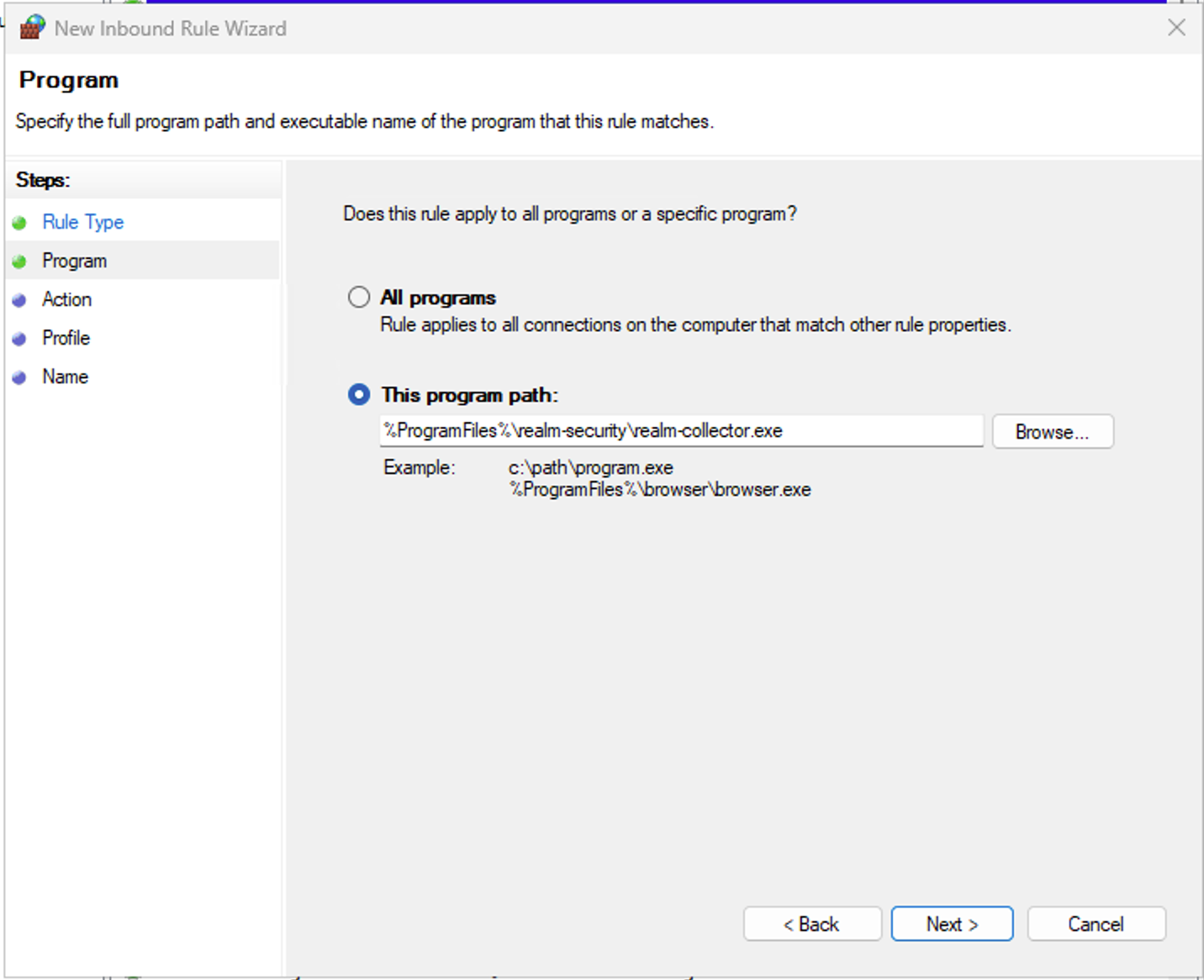
- Open Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security
- Create an inbound “Program” rule
- Program:
%ProgramFiles%\realm-security\realm-collector.exe - Action: Allow the connection
- Profile: Domain / Private / Public
- Name: Realm Collector
- If using hardware firewall appliance, open the necessary ports to the VM
- Required inbound ports are configurable in the Realm console
- Each syslog endpoint requires a unique port on the VM
Install on Linux
- Create a
realmuser to run the collector service
shell
sudo adduser realm- Download the latest Realm collector binary to
/usr/local/bin(v0.137.0-rlm4)
shell
curl https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/realm-security-public%2Fcollectors/packages/generic/realm-collector/v0.137.0-rlm4/realm-collector-linux-amd64 -o realm-collector && \
chmod 555 realm-collector && \
sudo chown realm:realm realm-collector && \
sudo mv realm-collector /usr/local/bin- Make sure the file was copied correctly
shell
sudo /usr/local/bin/realm-collector --version- Login as realm user
shell
sudo su - realm- Bootstrap collector with the install token
shell
/usr/local/bin/realm-collector --config realm:<YOUR_TOKEN_HERE>- If the collector install is successful, you should see something as follows
text
Installing Realm Collector v0.137.0-rlm4
Finalizing install with server
Fetching collector configuration
Realm Collector installed successfully- To test the collector is installed correctly, start the collector via CLI
shell
/usr/local/bin/realm-collector --config realm: --set=service.telemetry.logs.level=DEBUG 2>&1 | tee collector-debug.log- If the collector started successfully, you should see a log similar to below along with a bunch of debug logs
shell
info service@v0.126.0/service.go:289 Everything is ready. Begin running and processing data. {"resource": {}}- Next, stop the collector using ctrl-c and configure to run it as a service.
Run as a Service
Create a service for the collector (systemd), you must be logged in as root or a user with sudo permissions
- Create a system level service file in systemd
shell
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/realm-collector.serviceCopy the contents below into your new file
NOTE: Be sure to replace the
User=realmfield with the username of the user the collector service should run as
ini
[Unit]
Description=Realm Collector
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=realm
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/realm-collector --config realm:
Restart=always
RestartSec=1
# When healthy, the collector is quiet by design and logs
# very infrequently. Suppression can be helpful to avoid
# overwhelming journald in the event of a misconfigured
# integration causing errors receiving events.
LogRateLimitIntervalSec=1h
LogRateLimitBurst=100
# The following line can be commented out or deleted if
# all collector streams are configured with port > 1024.
AmbientCapabilities=CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target- Reload systemd, enable and start the collector service
shell
sudo systemctl daemon-reload && \
sudo systemctl enable --now realm-collector- Verify the service is up and running
shell
systemctl status realm-collector
sudo systemctl show -pUser,UID realm-collectorUpgrading
- Replace the Realm collector binary in
/usr/local/binwith the latest version (v0.137.0-rlm4)
shell
curl https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/realm-security-public%2Fcollectors/packages/generic/realm-collector/v0.137.0-rlm4/realm-collector-linux-amd64 -o realm-collector && \
chmod 555 realm-collector && \
sudo chown realm:realm realm-collector && \
sudo mv realm-collector /usr/local/bin- Restart the systemd service
shell
systemctl restart realm-collector- Verify the service is up and running
shell
systemctl status realm-collectorTroubleshooting
- View OTel config
shell
sudo su - realm
cat ~/.local/state/realmsec/otelcol.yaml- View collector logs
shell
journalctl -u realm-collector | less- Export collector logs to a file
shell
journalctl -u realm-collector > collector.log- Uninstall collector
To uninstall the collector, login as the root user
Stop the collector service
shell
sudo systemctl stop realm-collector- Delete collector binary and cleanup state
shell
sudo rm /usr/local/bin/realm-collector
sudo rm -r /home/realm/.local/state/realmsecUpdate Host Firewall
Ubuntu ships with UFW by default, albeit in a disabled state.
sudo ufw status -> if Status: inactive, no action required
Add collector port (replace PORT with the collector stream port from Realm):
sudo ufw allow PORTUpdate log sources
Update the on-prem log sources (Firewall/DNS router/Switches etc) to send logs to the collector.
See Fortigate guide for configuring Fortigate firewall to send data to the collector.
See Palo Alto guide for configuring Palo Alto firewall to send data to the collector.